Author: Barış Ataseven
Metabolism is a complex process that involves various chemical reactions and pathways that occur within an organism. These reactions are essential for maintaining life and include the breakdown of food into energy, the production and storage of nutrients, and the elimination of waste products.
The regulation of metabolism is crucial for maintaining the balance between energy intake and expenditure, and hormones play a key role in this process. Hormones are signalling molecules produced by endocrine glands that regulate various physiological processes, including metabolism.
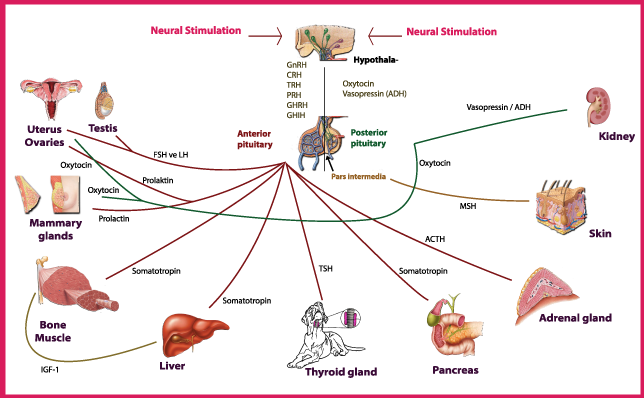
Insulin
Insulin is produced by the pancreas and is responsible for regulating glucose levels in the blood. When glucose levels rise, insulin is released to facilitate the uptake of glucose by cells for energy production or storage. Insulin also promotes the storage of excess glucose as glycogen in the liver and muscle cells.
Glucagon
Glucagon, on the other hand, is also produced by the pancreas, but it has the opposite effect of insulin. Glucagon stimulates the breakdown of glycogen in the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream when glucose levels are low. It also promotes the breakdown of fats in adipose tissue to release fatty acids for energy production.
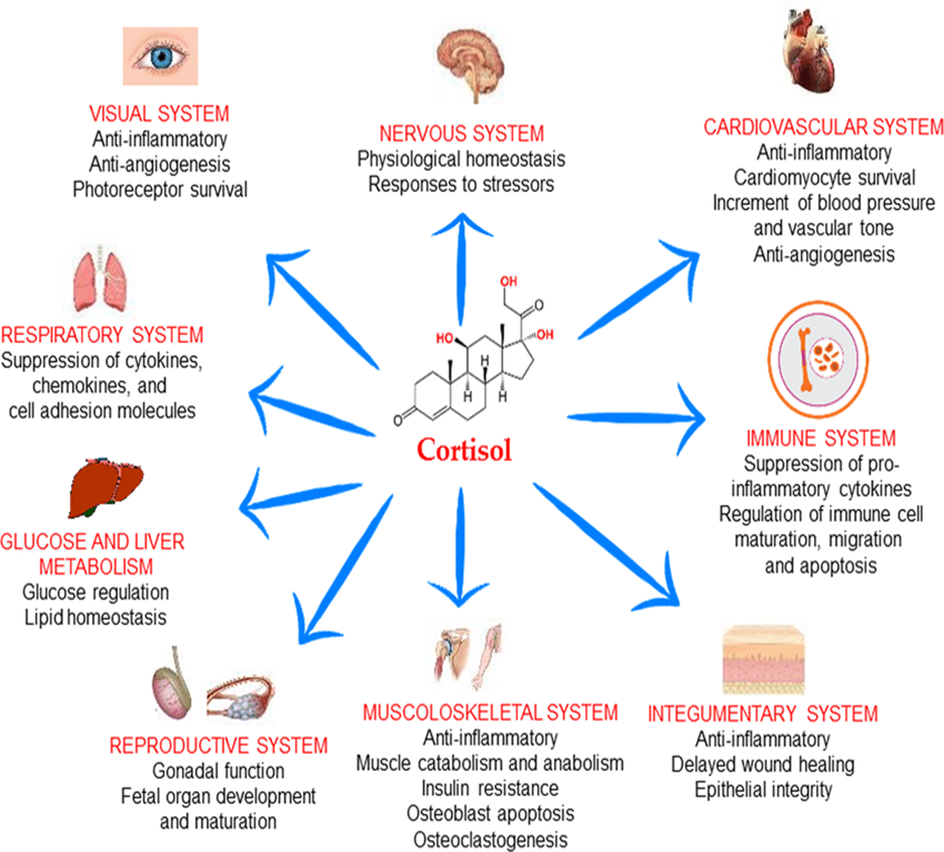
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. It plays a crucial role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Cortisol promotes the breakdown of proteins in muscle cells to release amino acids for gluconeogenesis, the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources. It also promotes the breakdown of fats in adipose tissue and the release of fatty acids for energy production.
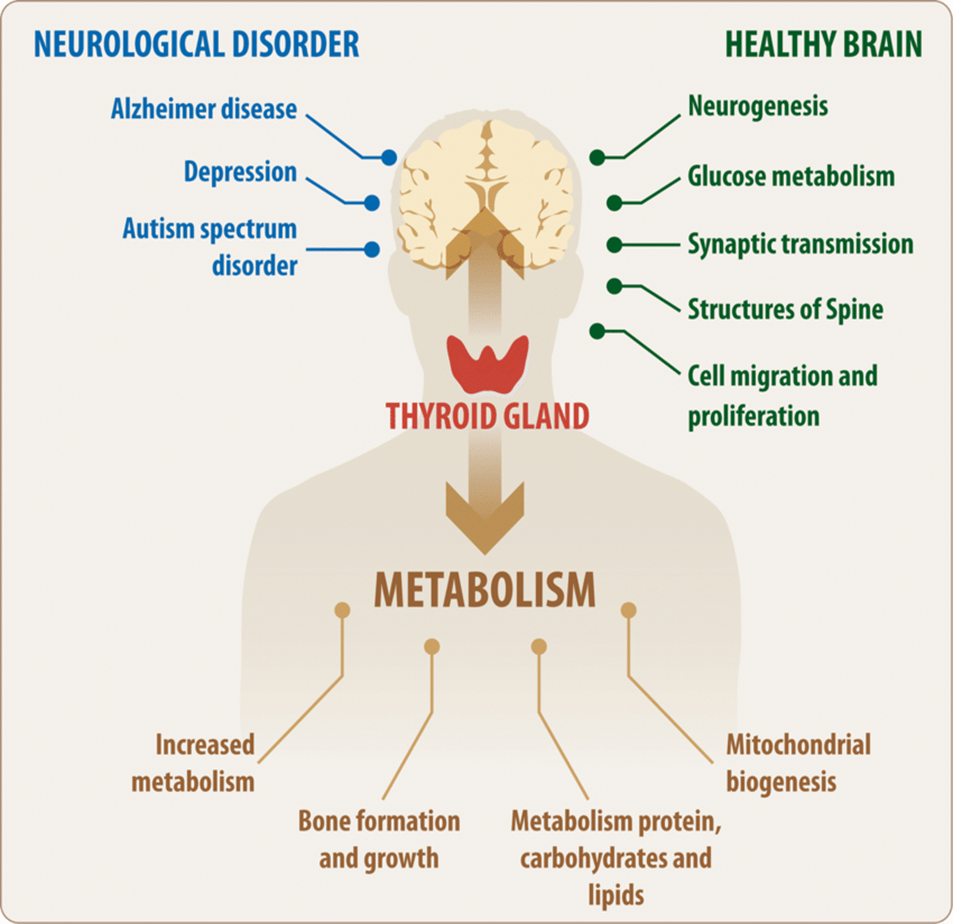
Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones, produced by the thyroid gland, play a critical role in the regulation of metabolism. They increase the metabolic rate by promoting the production of ATP, the energy currency of cells. Thyroid hormones also increase the activity of enzymes involved in carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism
Leptin
Leptin is another hormone that plays a crucial role in the regulation of metabolism. It is produced by adipose tissue and is involved in the regulation of energy balance. Leptin suppresses appetite and increases energy expenditure, promoting weight loss.
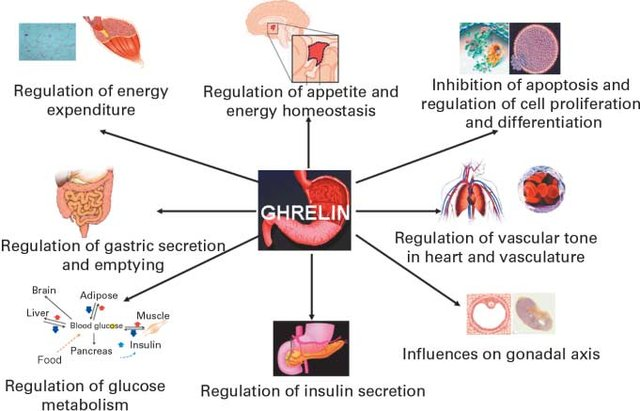
Ghrelin
Ghrelin is a hormone produced by the stomach that stimulates appetite and promotes food intake. It also plays a role in the regulation of energy balance by promoting the release of growth hormone, which increases the breakdown of fats for energy production.
Adiponectin
Adiponectin is a hormone produced by adipose tissue that regulates glucose and lipid metabolism. Adiponectin increases insulin sensitivity, promoting glucose uptake by cells for energy production. It also promotes the breakdown of fats in adipose tissue and the utilization of fatty acids for energy production.
In conclusion, hormones play a crucial role in the control of metabolism. Insulin and glucagon regulate glucose levels in the blood, while cortisol promotes the breakdown of proteins and fats for energy production.
Thyroid hormones increase the metabolic rate by promoting the production of ATP.
Leptin and ghrelin regulate appetite and energy balance, while adiponectin regulates glucose and lipid metabolism.
The proper regulation of hormones is essential for maintaining metabolic balance and overall health.
This article has been prepared from the presentation of our student Barış Ataseven.
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1472029917301728
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Role-of-cortisol-in-health-This-schematic-represents-the-roles-of-glucocorticoids_fig1_347540420
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Effects-of-thyroid-hormones-in-normal-and-pathologic-conditions-The-thyroid-gland-is-in_fig4_326785252
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nrn.2017.168
- https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Main-biological-functions-of-ghrelin-Ghrelin-is-mainly-synthesised-at-the-stomach-but-it_fig2_6865369
- https://www.google.com/search?q=adiponectin+function+in+metabolism&tbm=isch&ved=2ahUKEwi08uqTgqj-AhWBkKQKHbX7AXMQ2-cCegQIABAA&oq=adiponectin+function+in+metabolism&gs_lcp=CgNpbWcQAzoECCMQJ1DcBFiGFWDcFmgAcAB4AIAB6wGIAaoOkgEGMC4xMC4ymAEAoAEBqgELZ3dzLXdpei1pbWfAAQE&sclient=img&ei=_5A4ZPT2DoGhkgW194eYBw&bih=880&biw=1920#imgrc=vcoOV6L523DLFM
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/obesity-and-hormones#:~:text=The%20hormones%20leptin%20and%20insulin,the%20accumulation%20of%20body%20fat.